How to Obfuscate Long-Tail Keywords in SEO: Protect Your Strategy from Competitors
Introduction
Obfuscating long-tail keywords in SEO is a powerful, advanced yet often underutilized tactic to protect your keyword strategy from competitors who might reverse-engineer your content or keyword research.

In the hyper-competitive world of search engine optimization, savvy marketers and SEO strategists have begun to guard their secret sauce: their long-tail keyword strategy. These extended keyword phrases—often with low competition and high conversion potential—can be gold mines.
But once spotted by your competitors, they can be easily copied and used against you.
So how can you protect your SEO work? Obfuscation is the answer.
Keyword obfuscation is the strategic technique of disguising your long-tail keywords within your content and metadata so they’re harder to detect but still effective for search engines.
In this article, we’ll explore in detail how to obscure your long-tail SEO keywords, the rationale behind it, and how to strike a balance between SEO performance and competitive protection.
Table Of Contents:
- Why Obfuscate Long-Tail Keywords?
- What Is Keyword Obfuscation in SEO?
- Techniques to Obfuscate Long-Tail Keywords
- Tools That Competitors Use to Spy on Your Keywords in 2025
- Best Practices for Long-Term Obfuscation
- Case Study: A SaaS Brand Protecting Their SEO Edge
- Risks of Over-Obfuscation
- FAQs About Long-Tail Keyword Obfuscation
Why Obfuscate Long-Tail Keywords?
Finding high-performing long-tail keywords is getting harder than ever. These longer, more specific search phrases—like “best budget podcast microphone for beginners”—are gold for SEO.
They’re usually less competitive, easier to rank for, and often convert better because they match clear user intent. But here’s the catch: they’re not always obvious, and everyone wants them.
Most keyword research tools surface the same data for everyone. So once a low-competition long-tail keyword starts driving traffic, it’s only a matter of time before competitors discover it and create similar content.
That’s why some experienced SEOs resort to obfuscation techniques—deliberately hiding or masking their high-value keywords from casual scrapers or tools.
Long-tail keywords are often highly specific and generate targeted traffic. Unlike head terms (short, broad keywords), they bring in users with clear intent—which often means higher conversion rates.

By obfuscating your long-tail keywords, you:
- Protect intellectual property
- Maintain competitive advantage
- Avoid direct keyword cannibalization
- Reduce exposure to SEO scrapers
1. What Is Keyword Obfuscation in SEO?
Keyword obfuscation refers to the deliberate act of making your target keywords less obvious to competitors while still ensuring search engine bots can index and rank your content effectively.
This involves a mix of techniques, including:
- Semantic variation
- Partial keyword usage
- Embedding keywords in visual elements
- Utilizing schema markup
- Avoiding exact match domains and metadata exposure

2. Techniques to Obfuscate Long-Tail Keywords (With examples)
Here are advanced strategies to disguise your keyword targets effectively in 2025:
A. Use Synonyms and Semantic Alternatives
Instead of repeating the exact phrase (e.g., “best natural skincare products for acne-prone skin”), vary the language:
- Top organic face solutions for acne
- Natural remedies for acne-prone complexion
- Plant-based skincare tips for breakout-prone individuals

This semantic diversity not only makes it harder for competitors to spot your exact keyword but also satisfies Google’s semantic search algorithms.
B. Hide Keywords in Structured Data
Use Schema.org structured data to provide contextual relevance without placing keywords directly in visible content:
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Article",
"headline": "Ultimate Guide to Organic Skincare for Breakouts",
"keywords": ["acne-safe skincare", "natural acne treatment", "plant-based face care"]
}
C. Spread Keyword Variants Across Multiple Elements
Instead of putting the long-tail phrase in one place, split it across:
- Title tag: “The Ultimate Guide to Organic Skincare”
- Meta description: “Explore plant-based tips and acne-safe routines”
- H1: “Say Goodbye to Breakouts with Natural Solutions”
- Alt text: “acne-safe night routine”
This makes it less obvious to scraping tools but still readable by Google’s Natural Language Processing (NLP) algorithms.
D. Use Internal Linking With Anchored Variants
Don’t link with your exact match keywords. Use variations like:
- this natural skincare method
- plant-based acne solution
- breakout-friendly routine
This diversifies anchor text and protects your SEO strategy from being duplicated.
E. Embed Keywords in Images and Media
Use long-tail keywords in:
- Image alt tags
- Video metadata
- Infographic titles
- PDFs linked from your content
Since many SEO scraping tools don’t extract these media tags, they provide a layer of stealth.
F. Avoid Over-Optimization in Metadata
Search engines still use metadata like:
- Meta title
- Meta description
- URL structure
Make sure you’re not making it too easy to detect your keyword strategy here.
Example:
Instead of:/best-natural-skincare-products-acne-prone-skin
Use:/natural-skincare-guide-breakout-solutions
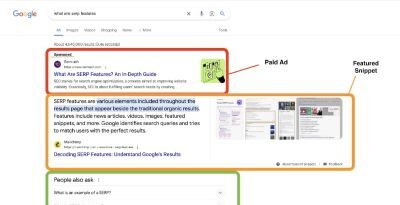
3. Tools That Competitors Use to Spy on Your Keywords in 2025
Ever wonder how some websites always seem to outrank you on Google? It’s not just luck—chances are, they’re using tools to peek behind the curtain and spy on your keyword strategy. The truth is, competitor keyword research is a common (and smart) tactic in SEO.
In this section, we’ll explore the most popular tools your competitors are using to track, analyze, and outrank your content—so you can level the playing field and even beat them at their own game.
To obfuscate effectively, know the tools you’re defending against. Here are the most common ones:
- SEMrush: Domain overview shows keyword ranking.
- Ahrefs Site Explorer: Reveals top pages and keyword traffic.
- Ubersuggest: Gives insight into estimated traffic and keyword density.
- SimilarWeb: Competitor traffic source breakdown.
- Surfer SEO: On-page keyword distribution and optimization.
- SpyFu: Competitor Spy Tool

Your goal is to break the pattern recognition these tools rely on.
4. Obfuscation vs. Cloaking: Know the Difference
Cloaking refers to showing different content to search engines than to users. It’s considered a black-hat SEO technique and is penalized by Google’s Webmaster Guidelines.
On the other hand, keyword obfuscation is ethical. You’re not deceiving users or bots—just being smart about how you present your strategy.
✅ Ethical
❌ Not deceptive
✅ SEO-friendly
✅ Google-compliant
5. Best Practices for Long-Term Obfuscation
✔️ Rotate Content Variants
Regularly update old content with keyword variants to avoid forming detectable patterns.
✔️ Avoid Common Keyword Stuffing
Overusing even variations can make your intent obvious. Keep usage natural.
✔️ Leverage LSI Keywords
Use Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) terms to maintain relevance without repetition.
Examples:
- Organic facial cleansers
- Herbal acne solutions
- Natural pore-tightening agents
✔️ Use Hidden Keywords in UX/UI
While you shouldn’t hide text (black-hat), you can include keywords in:
- Accordion menus
- Tabbed interfaces
- Tooltips
- Descriptive labels
✔️ Monitor Keyword Theft
Use tools like:
- SE Ranking
- Brand24
- BuzzSumo
Track if your content or phrasing is being copied and adjust your strategy accordingly.
6. Case Study: A SaaS Brand Protecting Their SEO Edge
A mid-sized SaaS company in the project management space had built strong SEO momentum by targeting ultra-specific long-tail keywords like:
- “best agile project management tool for non-tech teams”
- “remote-friendly sprint planning software for startups”
These niche, high-intent phrases were bringing in steady organic traffic and converting well—because the keywords were deeply aligned with their ideal customers’ pain points. But as their rankings improved, so did the attention from competitors using SEO spying tools like Ahrefs and SEMrush.
Soon, clone content started popping up, and their exact headers and titles were being mimicked almost word-for-word. Realizing that their carefully researched keyword strategy was being lifted, the team decided to act.
Here’s what they did to protect their SEO edge:
1. Semantic Obfuscation
They swapped out their exact-match headers and titles for semantically equivalent phrasing. For example, instead of using the header “Best Agile Project Management Tool for Non-Tech Teams,” they changed it to “Top Sprint Planning Solution for Cross-Functional Teams.”
This retained the meaning and intent, but made it harder for competitors to reverse-engineer their strategy using basic keyword scraping.
2. Structured Data Shielding
Instead of placing keyword-rich phrases openly in their copy, they moved strategic keyword clusters into schema markup (like FAQs, product descriptions, and HowTo schemas).
These keywords still signaled relevance to search engines but were less visible to casual scrapers and keyword tools.
3. Natural Language Diversification
They rewrote key landing pages using natural language processing (NLP) principles, making the content sound more like a human conversation and less like keyword stuffing. This both improved user experience and diluted keyword visibility to basic crawler tools.
4. Competitor Monitoring
They began tracking the backlink profiles and content updates of known competitors using SEO tools themselves—creating a feedback loop to stay one step ahead.
The Result?
While traffic dipped slightly during the first two weeks of the transition, it rebounded stronger. Rankings stabilized, competitor mimicry dropped off, and their team now has a defensible SEO moat based on intent-focused content rather than just keyword exposure.
7. Risks of Over-Obfuscation
Too much hiding can result in:
- Lower keyword relevance
- Confusion for crawlers
- Misaligned search intent
Strike a balance. Your keyword should be clear to Google, but less obvious to human competitors scanning your pages or using third-party tools.
8. Future of Keyword Obfuscation in AI-Driven SEO
As Google’s AI models (like MUM and BERT) continue to evolve, so does the sophistication of their content interpretation.
In the future, expect to rely more on:
- Contextual SEO
- Entity-based optimization
- Topical authority over keyword matching
This means obfuscation becomes easier—as Google cares more about topic depth and semantic relevance than exact match usage.
FAQs About Long-Tail Keyword Obfuscation
Final Thoughts
In a world where SEO competition is relentless and everyone is trying to steal a piece of your traffic, protecting your long-tail keywords is more than wise—it’s essential.
By implementing the techniques of keyword obfuscation, you preserve your strategic advantage while still playing by the rules of ethical SEO.
Remember, visibility in search engines should never mean visibility to competitors.
Let your content rise in rankings—without broadcasting your entire playbook.
If you’re serious about defending your SEO fortress, start integrating these obfuscation techniques today. And never underestimate the power of staying one step ahead in the search visibility game.

A digital marketer with over 10 years of experience, sharing insights on the Digital Marketing Blueprint Blog. Helping you master SEO, Social Media, and Online Promotion.